Spatial Data Analysis Enhances Urban Heat Island Mitigation Strategies
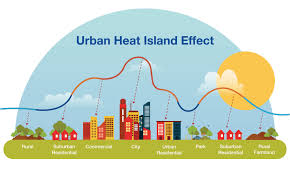
Urban Heat Islands (UHIs)—urban areas that experience significantly higher temperatures than their rural surroundings—pose a serious environmental and public health challenge, especially in the context of global climate change. In response, cities across the world are increasingly turning to spatial data analysis to understand and mitigate the UHI effect more effectively.
Spatial data analysis uses geospatial technologies such as GIS (Geographic Information Systems), remote sensing, and satellite imagery to analyze the spatial distribution of heat intensity, land use patterns, vegetation cover, and population density. This data-driven approach enables researchers, urban planners, and policymakers to make informed decisions and design targeted interventions that reduce surface and ambient temperatures in heat-vulnerable areas.
Recent studies have demonstrated that spatial analysis can accurately identify UHI hotspots at the neighborhood level. For instance, thermal satellite data can reveal areas with low vegetation and high impervious surface coverage—conditions that contribute to excessive heat retention. By overlaying socio-economic data, planners can also identify marginalized communities that are disproportionately affected by extreme heat, allowing for equitable climate resilience planning.
Mitigation strategies informed by spatial analysis include the implementation of green roofs, urban tree canopies, cool pavements, and reflective building materials. These measures not only reduce local temperatures but also improve air quality, enhance biodiversity, and promote energy efficiency. In cities like Singapore, Los Angeles, and Ahmedabad, such strategies are already being guided by real-time spatial data and predictive modeling.
Furthermore, spatial data tools enable continuous monitoring and evaluation of mitigation efforts, ensuring that interventions remain effective over time. They also support public engagement by visualizing environmental changes and the impact of urban heat.
In conclusion, spatial data analysis is a powerful tool in the fight against Urban Heat Islands. By integrating environmental science, technology, and policy-making, it supports smarter, more sustainable, and more inclusive urban development. As climate challenges intensify, embracing geospatial intelligence will be critical for building climate-resilient cities.
#SpatialDataAnalysis #UrbanHeatIsland #GeospatialTechnology #GIS #RemoteSensing #SmartCities #ClimateResilience #UrbanPlanning #HeatMitigation #GreenInfrastructure #SustainableCities #EnvironmentalPlanning #ThermalMapping #ClimateAdaptation #DataDrivenPlanning #UrbanForestry #GreenRoofs #CoolCities #SmartUrbanDesign #SatelliteImagery #GeoAnalytics #HeatVulnerability #ClimateJustice #UrbanClimate #ResilientCities #CityPlanning #SpatialThinking #EcoUrbanism #SustainableDevelopment #Geoinformatics
Website link: youngscientistawards.com NominationLink:https://youngscientistawards.com/awardnomination/ecategory=Awards&rcategoryrdee
Contact Us: support@youngscientistawards.com
___________________________________
Social Media:
Twitter : https://twitter.com/youngsc06963908
Linkedin- : https://www.linkedin.com/in/shravya-r...
Pinterest : https://in.pinterest.com/youngscienti...
Blog : https://youngscientistaward.blogspot....
Tumblr : https://www.tumblr.com/blog/shravya9



Comments
Post a Comment